External benefits can arise from both production and consumption. What is external benefit.
A an external cost.
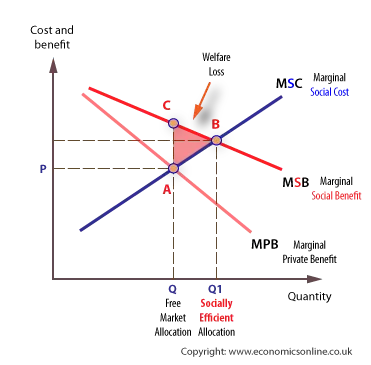
. An external benefit is the benefit gained by an individual or firm as a result of an economic transaction but where they are not directly involved in the transaction. What is an external benefit. B an external benefit.
B additional cost of producing an additional good. When there are neither external benefits nor external costs. External benefit definition.
1 An externality is. In other words it is a cost imposed on a party that cannot control whether or not the transaction or activity occurs. An external benefit is a benefit from a good or service that someone other than the consumer receives.
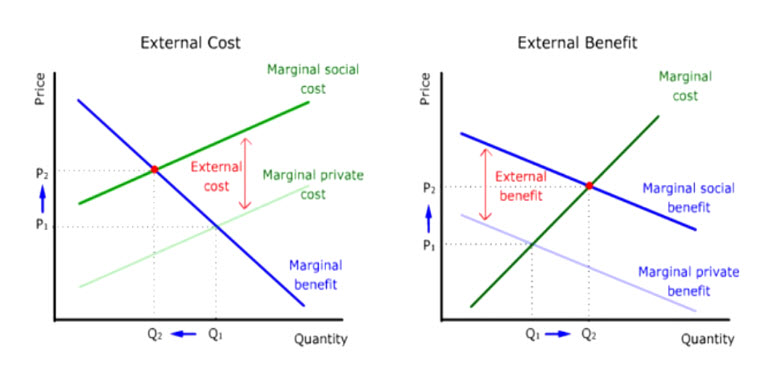
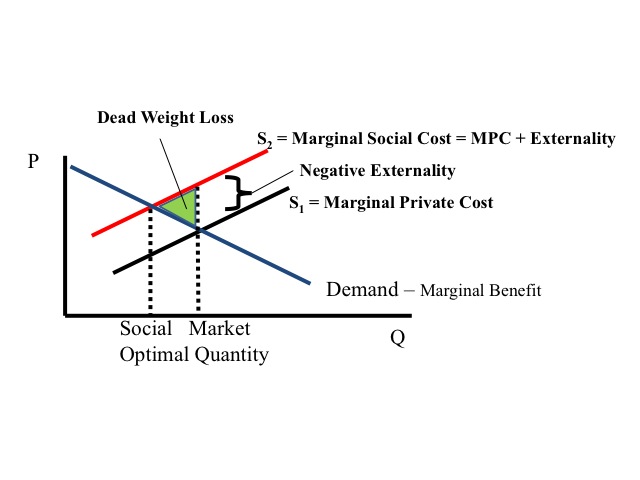
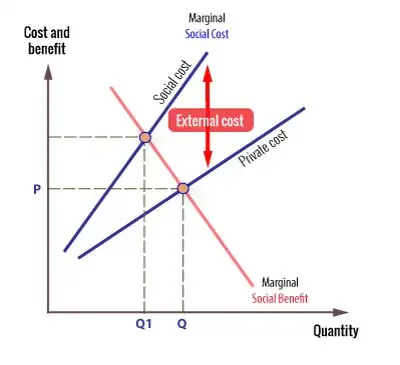
_____ benefit can be defined as the benefits to all of society. Positive externalities are the benefits of things negative externalities are its costs disadvanatges. B the total cost to society of producing an additional unit of a good or service.
A benefit from a good experienced by someone other than the person who buys the good. A marginal external benefit. Bestowed on parties outside the activity or transaction.
A cost of an activity received by people other than those who pursue the activity production or consumption. It can be calculated as the difference between _____ benefit and the _____ benefit. See the answer See the answer done loading.
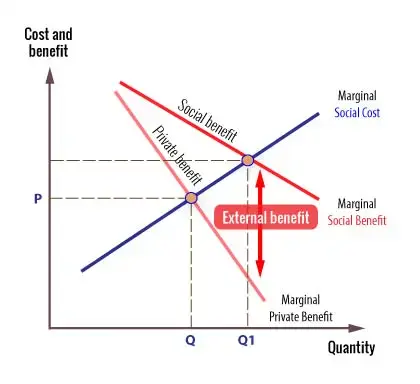
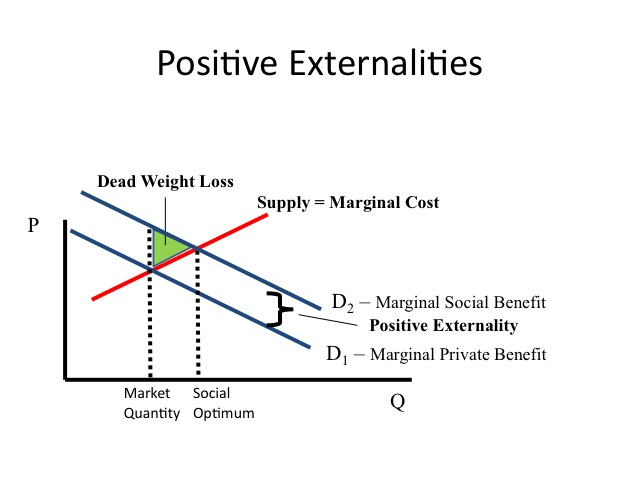
A positive externality is a _____ to a _____ party to an economic transaction outside the _____ mechanism. The difference between the marginal social benefit curve and the market demand curve is the. Certain potential market transactions may have positive external benefits for others who are not directly involved in the transaction.
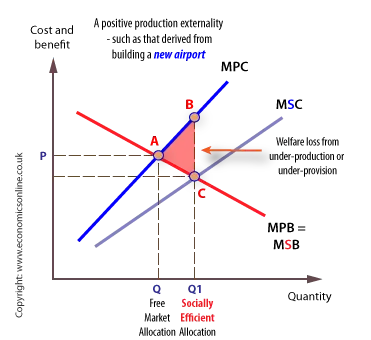
B system of rose production permits. Deadweight loss due to external benefits. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either consumer or producer market transactions.
An _____ is a cost or benefit accruing to an individual or groupa third-party that is external to a market transaction. However these transactions do not occur because they do not offer a net benefit to the parties involved in the transaction. Externalities in Our Lives An externality is an unintended cost or benefit of an activity that affects a third party Positive Externality.
By paying college students a subsidy equal to the external benefit from a college education the government will cause students to internalize the externality. A benefit of an activity received by people other than those who pursue the activity production or consumption Negative Externality. The Tax Reform Act of 1969 played a key role in defining private.
An external cost or negative externality is a cost that a transaction or activity imposes on a party that is not part of the transaction or activity. Less pollution is a probable result. A marginal external benefit is the benefit from an additional unit of a good or service that people other than the consumer enjoy.
If polluters are charged to pollute then. Fill in the missing words. It describes a situation where a foundation insider is engaged in a financial transaction as the provider and receiver of the benefit.
The effect is that a director must consider the commercial benefit to the company when considering whether or not to enter into transactions. The purpose of this blog is detail how a subject to transaction benefits the homeowners. The complementary notion is that of external benefit or positive externality.
D a private good 73 Which of the following often involves external benefits. Positive externalities or external benefit 1. A reduction in transaction costs.
There are many benefits to the homeowner as well and being able to convey these benefits will help the new investor secure a real estate transaction. A a cost or benefit resulting from some activity or transaction that is imposed or. C marginal external cost.
It is the negative enternality cost that a. External beneficiaries are collectively called third parties. Externality The ________________ curve for positive externalities reflects only the direct private benefit to the individuals who consume it.
C a public good. An external benefit is a benefit that one person gains due to another persons actions. In the context of private benefit transactions for nonprofits self-dealing is a term that applies to private foundations.
In economics an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another partys or parties activity. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. An external benefit is sometimes referred to as a positive externality and is defined as the benefit that a particular transaction offers to a party that is not involved in the transaction.
One thing that is often forgotten when guarantees are being taken from group companies is that for the purposes of the Act it is not enough for the guarantee to benefit the group there should be benefit. A water pollution B polio vaccine C tobacco smoking D drunken driving 74 If production of a product causes sizable external benefits an appropriate government policy might be to. That is the external benefit from a college education will become a private benefit received by college students and the demand curve for college educations will shift from D1 to D2.
Is a cost or a benefit accruing to an individual group or a third party that is external to a market transaction. Sellers primarily benefit from a subject-to transaction in the following ways. _____ benefit can be defined as the benefits to the.
Living Economics External Benefit And External Cost Transcript

0 Comments